ArgoCD核心组件源码浅析
在上一章ArgoCD的设计与功能中,我们介绍了与ArgoCD相关的抽象概念:GitOps、IaC、DevOps,并梳理了ArgoCD的核心组件:Application Controller、Repository Server、API Server
由于API Server的功能在于提供RPC/REST接口和UI界面展示集群资源状态,与GitOps的实现关系不大(正如Core部署模式去掉了API Server),本文将从源码角度分析ArgoCD组件Application Controller、Repository Server的功能实现。
Application Controller
Application(以下简称App)是ArgoCD在K8S中注册的自定义资源(CRD),App Controller是ArgoCD实现的K8S控制器,它连续监视App CR, 并将CR中描述的期望状态和集群实际状态对比,若不一致,将采取纠正措施将二者同步。ArgoCD将集群连接信息和部署的项目信息以及资源清单渲染参数存入了Application CR中,一个最小化的App如下:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: guestbook
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/argoproj/argocd-example-apps.git
targetRevision: HEAD
path: guestbook
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: guestbook
其中source表示git仓库和部署项目路径分析信息,destination表示部署的目标集群,在argocd中,可以有多个项目和集群被管理,他们的信息以k8s资源secret的形式存储在etcd中:
// cluster info
apiVersion: v1
data:
config: ... // 身份信息、用于TLS双向验证的对端CA证书
name: cluster-1 // 集群名
server: ... // 目标集群API Server的URL
kind: Secret
metadata:
annotations:
managed-by: argocd.argoproj.io
creationTimestamp: "2022-08-05T03:14:07Z"
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: cluster
name: cluster-1
namespace: argocd
resourceVersion: "443946"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/argocd/secrets/cluster-1
uid: b6f3ff89-782d-426e-aeaf-0c431f7f84bb
type: Opaque
// project info
apiVersion: v1
data:
name: Zmxhbm5lbA==
sshPrivateKey: ... // 拉取 ssh repo的私钥
type: Z2l0
url: ... // repo ssh url
kind: Secret
metadata:
annotations:
managed-by: argocd.argoproj.io
creationTimestamp: "2022-09-26T07:25:33Z"
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: repository
name: flannel
namespace: argocd
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: apps.robocloud.autowise.ai/v1alpha1
blockOwnerDeletion: true
controller: true
kind: Project
name: flannel
uid: 6f98130d-8e32-4ddb-9e56-02586e5debbd
resourceVersion: "121649320"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/argocd/secrets/flannel
uid: 06cfa628-c0a0-4a0e-b15e-ec3cca97e281
type: Opaque
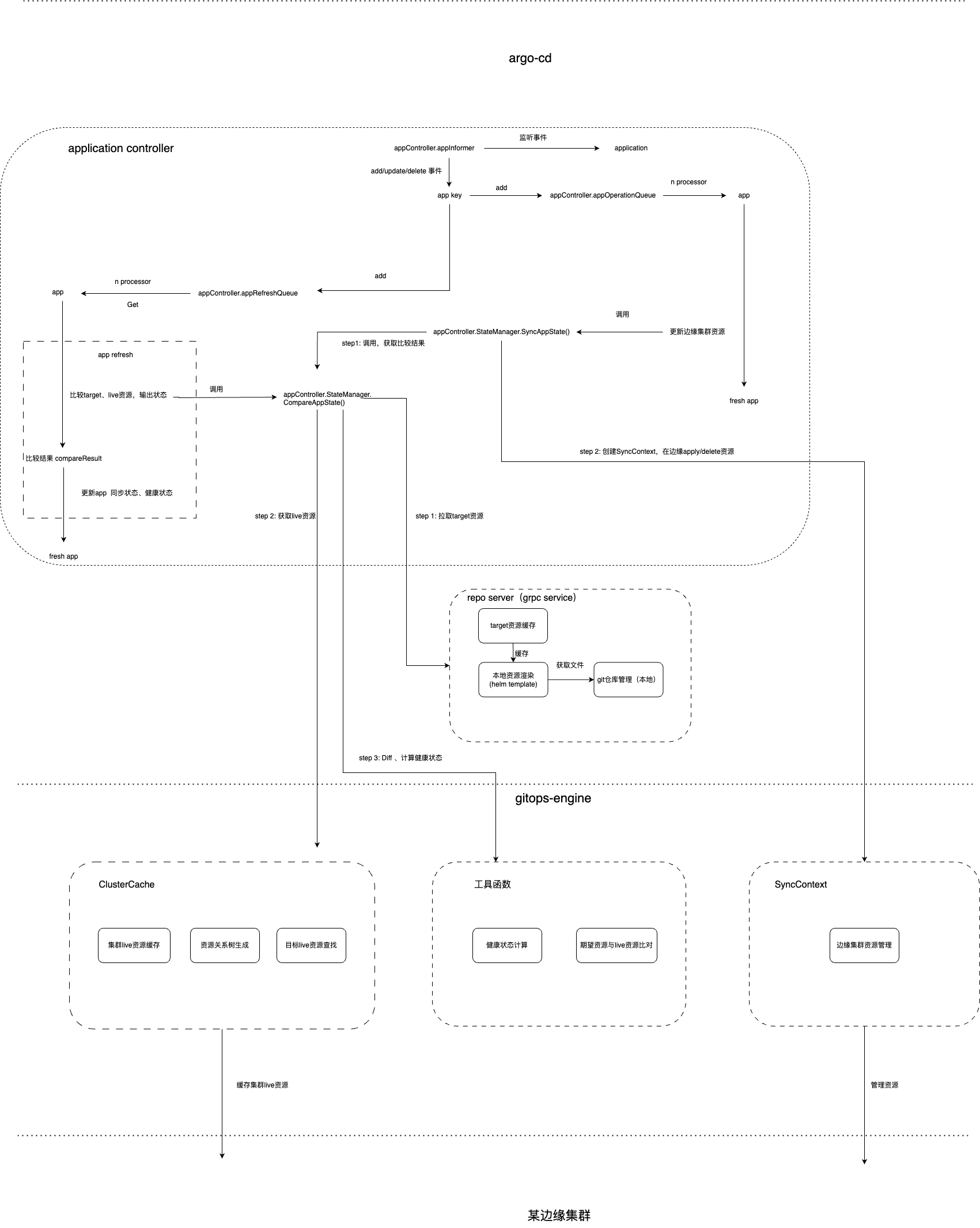
Argocd的Application Controller Run方法一些重要的步骤我以注释的形式解释:
// Run starts the Application CRD controller.
func (ctrl *ApplicationController) Run(ctx context.Context, statusProcessors int, operationProcessors int) {
...
defer ctrl.appRefreshQueue.ShutDown() // app 刷新队列,生产者添加待刷新app的key,消费者负责向git repo获取最新的资源期望状态,与集群当前状态做diff,更新app的sync status和health status
defer ctrl.appOperationQueue.ShutDown() // app 同步队列,生产者添加需要同步的app的key,消费者负责执行同步任务
...
go ctrl.appInformer.Run(ctx.Done()) // 运行AppInformer, watch到的app add/update/delete事件会被加入到工作队列appReFreshQueue、appOperationQueue中等待worker处理
...
// argocd 提供启动参数status processors参数配置AppRefreshQueue消费者worker的数量
for i := 0; i < statusProcessors; i++ {
go wait.Until(func() {
for ctrl.processAppRefreshQueueItem() {
}
}, time.Second, ctx.Done())
}
// 同上,提供operation processors参数配置AppOperationQueue消费者worker数量
for i := 0; i < operationProcessors; i++ {
go wait.Until(func() {
for ctrl.processAppOperationQueueItem() {
}
}, time.Second, ctx.Done())
}
...
<-ctx.Done()
}
值得一提的是,argocd开发operator与一般k8s二开operator有些不同:前者使用client-go实现了sharedIndexInformer(appInformer)并单独使用workqueue,后者使用operator开发框架kubebuilder结合controller-manager填充Reconcile方法,可能因为argocd项目启动时间早于kubebuilder GA的时间。
在上面的代码分析中,我们可以得知app对应两个workqueue:appRefreshQueue、appOperationQueue,以及对应的处理方法:processAppRefreshQueueItem(), ctrl.processAppOperationQueueItem()
下面我们从队列的生产者角度分析,触发生产者向队列添加元素的事件有哪些
查阅代码可知函数调用链:
// controller/appcontroller.go
// 1. app有add/update/delete事件时
NewApplicationController
ctrl.newApplicationInformerAndLister
informer.AddEventHandler
AddFunc
ctrl.appRefreshQueue.AddRateLimited
ctrl.appOperationQueue.AddRateLimited
UpdateFunc
ctrl.requestAppRefresh
ctrl.appRefreshQueue.Add
ctrl.appOperationQueue.Add
ctrl.appOperationQueue.AddRateLimited
DeleteFunc
ctrl.appRefreshQueue.Add
// 2. ArgoCD监听的集群状态缓存statecache有变动时,触发对应app key入队
NewApplicationController
statecache.NewLiveStateCache
ctrl.handleObjectUpdated
ctrl.requestAppRefresh
ctrl.appRefreshQueue.Add
ctrl.appOperationQueue.Add
// 3. 开启自动同步的app进入OutOfSync状态尝试同步时
NewApplicationController
ctrl.processAppRefreshQueueItem
ctrl.autoSync
ctrl.requestAppRefresh
ctrl.appRefreshQueue.Add
ctrl.appOperationQueue.Add
// server/application/application.go
// 4 ArgoCD API Server实现了GRPC接口Get, 上游方法(ManagedResources getAppResources)调用时直接向云端K8S API Server发送Patch请求更新annotaion,触发App更新,进而触发App调谐
server.ManagedResources
server.getAppResources
server.getCachedAppState
server.Get
RefreshApp
appIf.Patch
总结有以下几个操作会触发app的refresh和sync:
- ArgoCD UI使用时未找到集群缓存资源、手动refresh、sync
- App资源有Create/Update/Delete事件
- App自动同步重试
- 管理的集群资源缓存更新
集群状态缓存
上文我们提到目标集群资源缓存也会触发app的refresh、sync。也就是说argocd与目标集群建立了长连接,来watch集群内受argocd自身管控的资源的状态,有意思的是,ArgoCD贡献者没有直接实现clusterCache组件,而是引用了一个库gitops-engine的cache类实现,结构的字段数量太多,若有兴趣查阅ClusterCache struct
经过对gitops-engine的源码梳理,clusterCache同步集群资源状态主要有两个方法 EnsureSynced、Invalidated。EnsureSync先获取目标集群的API Resource, 再为每个API Resource创建dynamic client, 调用List方法初始化缓存,watch方法持续更新缓存,Invalidate关闭channel中止相关协程:

看的出ArgoCD监听集群资源状态的协程数量大于等于目标集群的API资源的数量,较占用协程资源,好在API Server支持Http2,watch机制支持多路复用,所以本机文件描述符/socket的消耗不算多。
gitops-engine clusterCache提供了Invalidate方法中止状态同步,但是ArgoCD在使用gitops-engine这套机制的时候没有直接暴露出可以停止clusterCache list&watch协程的api,相关配置就一个app的状态同步最大超时次数,也就是app的refresh retry次数达到指定的最大值时,app便不会继续retry,需要修改Application的字段或者在UI手动触发refresh,这对弱网环境的集群来讲并不友好,因为集群断连后在ArgoCD的refresh retry期间,ArgoCD的refreshQueue会瞬间被塞满大量的key,导致后面一些能正常连接的集群的refresh请求没法及时处理,对应的现象是UI上Refresh button一直在loading,同时资源状态未更新,影响DevOps的效率。
集群期望状态
GitOps的核心逻辑是比较实际状态和期望状态,根据diff的结果决策资源的更新逻辑,而期望状态需要从git仓库中获取。ArgoCD为git和资源渲染工具helm/kustomize封装成了方法,作为gRPC服务供其他组件调用,这是我们后面要分析的组件Repository Server。
而App Controller作为Repo Server的gRPC Client端,在该方法中获取并比较了实际状态和期望状态:
// controller/state.go
// CompareAppState compares application git state to the live app state, using the specified
// revision and supplied source. If revision or overrides are empty, then compares against
// revision and overrides in the app spec.
func (m *appStateManager) CompareAppState(app *v1alpha1.Application, project *v1alpha1.AppProject, revisions []string, sources []v1alpha1.ApplicationSource, noCache bool, noRevisionCache bool, localManifests []string, hasMultipleSources bool) *comparisonResult {
if len(localManifests) == 0 {
// If the length of revisions is not same as the length of sources,
// we take the revisions from the sources directly for all the sources.
if len(revisions) != len(sources) {
revisions = make([]string, 0)
for _, source := range sources {
revisions = append(revisions, source.TargetRevision)
}
}
targetObjs, manifestInfos, err = m.getRepoObjs(app, sources, appLabelKey, revisions, noCache, noRevisionCache, verifySignature, project)
...
} else {
// Prevent applying local manifests for now when signature verification is enabled
// This is also enforced on API level, but as a last resort, we also enforce it here
if gpg.IsGPGEnabled() && verifySignature {
...
} else {
targetObjs, err = unmarshalManifests(localManifests)
...
}
// empty out manifestInfoMap
manifestInfos = make([]*apiclient.ManifestResponse, 0)
}
...
liveObjByKey, err := m.liveStateCache.GetManagedLiveObjs(app, targetObjs)
...
reconciliation := sync.Reconcile(targetObjs, liveObjByKey, app.Spec.Destination.Namespace, infoProvider)
ts.AddCheckpoint("live_ms")
...
diffResults, err := argodiff.StateDiffs(reconciliation.Live, reconciliation.Target, diffConfig)
if err != nil {
diffResults = &diff.DiffResultList{}
failedToLoadObjs = true
msg := fmt.Sprintf("Failed to compare desired state to live state: %s", err.Error())
conditions = append(conditions, v1alpha1.ApplicationCondition{Type: v1alpha1.ApplicationConditionComparisonError, Message: msg, LastTransitionTime: &now})
}
ts.AddCheckpoint("diff_ms")
syncCode := v1alpha1.SyncStatusCodeSynced
managedResources := make([]managedResource, len(reconciliation.Target))
resourceSummaries := make([]v1alpha1.ResourceStatus, len(reconciliation.Target))
for i, targetObj := range reconciliation.Target {
liveObj := reconciliation.Live[i]
obj := liveObj
if obj == nil {
obj = targetObj
}
if obj == nil {
continue
}
gvk := obj.GroupVersionKind()
isSelfReferencedObj := m.isSelfReferencedObj(liveObj, targetObj, app.GetName(), appLabelKey, trackingMethod)
resState := v1alpha1.ResourceStatus{
Namespace: obj.GetNamespace(),
Name: obj.GetName(),
Kind: gvk.Kind,
Version: gvk.Version,
Group: gvk.Group,
Hook: hookutil.IsHook(obj),
RequiresPruning: targetObj == nil && liveObj != nil && isSelfReferencedObj,
}
if targetObj != nil {
resState.SyncWave = int64(syncwaves.Wave(targetObj))
}
var diffResult diff.DiffResult
if i < len(diffResults.Diffs) {
diffResult = diffResults.Diffs[i]
} else {
diffResult = diff.DiffResult{Modified: false, NormalizedLive: []byte("{}"), PredictedLive: []byte("{}")}
}
// For the case when a namespace is managed with `managedNamespaceMetadata` AND it has resource tracking
// enabled (e.g. someone manually adds resource tracking labels or annotations), we need to do some
// bookkeeping in order to ensure that it's not considered `OutOfSync` (since it does not exist in source
// control).
//
// This is in addition to the bookkeeping we do (see `isManagedNamespace` and its references) to prevent said
// namespace from being pruned.
isManagedNs := isManagedNamespace(targetObj, app) && liveObj == nil
if resState.Hook || ignore.Ignore(obj) || (targetObj != nil && hookutil.Skip(targetObj)) || !isSelfReferencedObj {
// For resource hooks, skipped resources or objects that may have
// been created by another controller with annotations copied from
// the source object, don't store sync status, and do not affect
// overall sync status
} else if !isManagedNs && (diffResult.Modified || targetObj == nil || liveObj == nil) {
// Set resource state to OutOfSync since one of the following is true:
// * target and live resource are different
// * target resource not defined and live resource is extra
// * target resource present but live resource is missing
resState.Status = v1alpha1.SyncStatusCodeOutOfSync
// we ignore the status if the obj needs pruning AND we have the annotation
needsPruning := targetObj == nil && liveObj != nil
if !(needsPruning && resourceutil.HasAnnotationOption(obj, common.AnnotationCompareOptions, "IgnoreExtraneous")) {
syncCode = v1alpha1.SyncStatusCodeOutOfSync
}
} else {
resState.Status = v1alpha1.SyncStatusCodeSynced
}
// set unknown status to all resource that are not permitted in the app project
isNamespaced, err := m.liveStateCache.IsNamespaced(app.Spec.Destination.Server, gvk.GroupKind())
if !project.IsGroupKindPermitted(gvk.GroupKind(), isNamespaced && err == nil) {
resState.Status = v1alpha1.SyncStatusCodeUnknown
}
if isNamespaced && obj.GetNamespace() == "" {
conditions = append(conditions, v1alpha1.ApplicationCondition{Type: v1alpha1.ApplicationConditionInvalidSpecError, Message: fmt.Sprintf("Namespace for %s %s is missing.", obj.GetName(), gvk.String()), LastTransitionTime: &now})
}
// we can't say anything about the status if we were unable to get the target objects
if failedToLoadObjs {
resState.Status = v1alpha1.SyncStatusCodeUnknown
}
resourceVersion := ""
if liveObj != nil {
resourceVersion = liveObj.GetResourceVersion()
}
managedResources[i] = managedResource{
Name: resState.Name,
Namespace: resState.Namespace,
Group: resState.Group,
Kind: resState.Kind,
Version: resState.Version,
Live: liveObj,
Target: targetObj,
Diff: diffResult,
Hook: resState.Hook,
ResourceVersion: resourceVersion,
}
resourceSummaries[i] = resState
}
...
compRes := comparisonResult{
syncStatus: &syncStatus,
healthStatus: healthStatus,
resources: resourceSummaries,
managedResources: managedResources,
reconciliationResult: reconciliation,
diffConfig: diffConfig,
diffResultList: diffResults,
}
...
return &compRes
}
获取CompareResult之后,appController调用SyncAppState方法创建gitops-engine中另一个类SyncContext,为目标集群apply/delete资源。
Repository Server
repo server是ArgoCD获取表达期望状态的资源清单数据源,该服务封装了版本控制工具git和一系列资源模板渲染工具helm、kustomize,作为gRPC服务暴露给其他组件调用。repo server实现的接口不多:
// reposerver/repository/repository.proto
// ManifestService
service RepoServerService {
// GenerateManifest generates manifest for application in specified repo name and revision
rpc GenerateManifest(ManifestRequest) returns (ManifestResponse) {
}
// GenerateManifestWithFiles generates manifest for application using provided tarball of files
rpc GenerateManifestWithFiles(stream ManifestRequestWithFiles) returns (ManifestResponse) {
}
// Returns a bool val if the repository is valid and has proper access
rpc TestRepository(TestRepositoryRequest) returns (TestRepositoryResponse) {
}
// Returns a valid revision
rpc ResolveRevision(ResolveRevisionRequest) returns (ResolveRevisionResponse) {
}
// Returns a list of refs (e.g. branches and tags) in the repo
rpc ListRefs(ListRefsRequest) returns (Refs) {
}
// ListApps returns a list of apps in the repo
rpc ListApps(ListAppsRequest) returns (AppList) {
}
// ListPlugins returns a list of cmp v2 plugins running as sidecar to reposerver
rpc ListPlugins(google.protobuf.Empty) returns (PluginList) {
}
// Generate manifest for application in specified repo name and revision
rpc GetAppDetails(RepoServerAppDetailsQuery) returns (RepoAppDetailsResponse) {
}
// Get the meta-data (author, date, tags, message) for a specific revision of the repo
rpc GetRevisionMetadata(RepoServerRevisionMetadataRequest) returns (github.com.argoproj.argo_cd.v2.pkg.apis.application.v1alpha1.RevisionMetadata) {
}
// Get the chart details (author, date, tags, message) for a specific revision of the repo
rpc GetRevisionChartDetails(RepoServerRevisionChartDetailsRequest) returns (github.com.argoproj.argo_cd.v2.pkg.apis.application.v1alpha1.ChartDetails) {
}
// GetHelmCharts returns list of helm charts in the specified repository
rpc GetHelmCharts(HelmChartsRequest) returns (HelmChartsResponse) {
}
// GetGitFiles returns a set of file paths and their contents for the given repo
rpc GetGitFiles(GitFilesRequest) returns (GitFilesResponse) {
}
// GetGitDirectories returns a set of directory paths for the given repo
rpc GetGitDirectories(GitDirectoriesRequest) returns (GitDirectoriesResponse) {
}
}
我比较熟悉的git repo存储资源形式为helm charts,在argocd配置helm的参数后,它会调用repo server的GenerateManifest方法使用helm参数(parameter valueFile等)渲染出可直接部署的k8s资源清单,ArgoCD内置了helm二进制文件,并封装了主要命令helm template:
// util/helm/helm.go
// Helm provides wrapper functionality around the `helm` command.
type Helm interface {
// Template returns a list of unstructured objects from a `helm template` command
Template(opts *TemplateOpts) (string, error)
// GetParameters returns a list of chart parameters taking into account values in provided YAML files.
GetParameters(valuesFiles []pathutil.ResolvedFilePath, appPath, repoRoot string) (map[string]string, error)
// DependencyBuild runs `helm dependency build` to download a chart's dependencies
DependencyBuild() error
// Init runs `helm init --client-only`
Init() error
// Dispose deletes temp resources
Dispose()
}
repo server对git则混合使用了git二进制文件和go-git/v5库实现git仓库的本地管理,git client和实现的方法:
type Client interface {
Root() string
Init() error
Fetch(revision string) error
Submodule() error
Checkout(revision string, submoduleEnabled bool) error
LsRefs() (*Refs, error)
LsRemote(revision string) (string, error)
LsFiles(path string, enableNewGitFileGlobbing bool) ([]string, error)
LsLargeFiles() ([]string, error)
CommitSHA() (string, error)
RevisionMetadata(revision string) (*RevisionMetadata, error)
VerifyCommitSignature(string) (string, error)
IsAnnotatedTag(string) bool
}
// nativeGitClient implements Client interface using git CLI
type nativeGitClient struct {
EventHandlers
// URL of the repository
repoURL string
// Root path of repository
root string
// Authenticator credentials for private repositories
creds Creds
// Whether to connect insecurely to repository, e.g. don't verify certificate
insecure bool
// Whether the repository is LFS enabled
enableLfs bool
// gitRefCache knows how to cache git refs
gitRefCache gitRefCache
// indicates if client allowed to load refs from cache
loadRefFromCache bool
// HTTP/HTTPS proxy used to access repository
proxy string
}
我们知道,git版本控制有四个区:工作区、暂存区、版本库、远程仓库。我们平时存放代码的地方叫工作区,ArgoCD也需要依赖git checkout命令更新工作区的文件为指定分支。所以在repo server提取资源清单时,只能单线程同步操作不同commit下的文件,所以粗粒度控制本地git repo的方式时为每一个相同的repo增加互斥锁,仅支持同步操作,但是在操作相同commit是可以支持并发的,repo server使用一个stateMap和sync.Cond实现了:
func NewRepositoryLock() *repositoryLock {
return &repositoryLock{stateByKey: map[string]*repositoryState{}}
}
type repositoryLock struct {
lock sync.Mutex
stateByKey map[string]*repositoryState
}
// Lock acquires lock unless lock is already acquired with the same commit and allowConcurrent is set to true
func (r *repositoryLock) Lock(path string, revision string, allowConcurrent bool, init func() (io.Closer, error)) (io.Closer, error) {
r.lock.Lock()
state, ok := r.stateByKey[path]
if !ok {
state = &repositoryState{cond: &sync.Cond{L: &sync.Mutex{}}}
r.stateByKey[path] = state
}
r.lock.Unlock()
closer := ioutil.NewCloser(func() error {
state.cond.L.Lock()
notify := false
state.processCount--
var err error
if state.processCount == 0 {
notify = true
state.revision = ""
err = state.initCloser.Close()
}
state.cond.L.Unlock()
if notify {
state.cond.Broadcast()
}
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("init closer failed: %w", err)
}
return nil
})
for {
state.cond.L.Lock()
if state.revision == "" {
// no in progress operation for that repo. Go ahead.
initCloser, err := init()
if err != nil {
state.cond.L.Unlock()
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to initialize repository resources: %w", err)
}
state.initCloser = initCloser
state.revision = revision
state.processCount = 1
state.allowConcurrent = allowConcurrent
state.cond.L.Unlock()
return closer, nil
} else if state.revision == revision && state.allowConcurrent && allowConcurrent {
// same revision already processing and concurrent processing allowed. Increment process count and go ahead.
state.processCount++
state.cond.L.Unlock()
return closer, nil
} else {
state.cond.Wait()
// wait when all in-flight processes of this revision complete and try again
state.cond.L.Unlock()
}
}
}
type repositoryState struct {
cond *sync.Cond
revision string
initCloser io.Closer
processCount int
allowConcurrent bool
}
总结
在许久之前阅读ArgoCD源码时画过一张函数调用草图,希望能形象地展示其中函数和组件调用关系: